Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is changing how people manage money. It uses blockchain technology to create financial services without banks or other middlemen. DeFi lets users lend, borrow, and trade directly with each other through smart contracts.
DeFi aims to make financial services open to everyone with an internet connection. It removes the need for traditional banks and financial companies. This can lead to lower fees and more access to services. Users keep control of their own funds instead of trusting a bank.
The DeFi world is growing fast. In 2020, the total value of assets in DeFi grew from $1 billion to over $20 billion. New DeFi apps and services appear often. These range from lending platforms to decentralized exchanges where people trade cryptocurrencies. While exciting, DeFi also comes with risks that users should understand before jumping in.

Top 10 DeFi Apps
| Rank | App | Category | Blockchain | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lido | Liquid Staking | Ethereum | Stake your ETH and earn rewards without locking up your assets. |
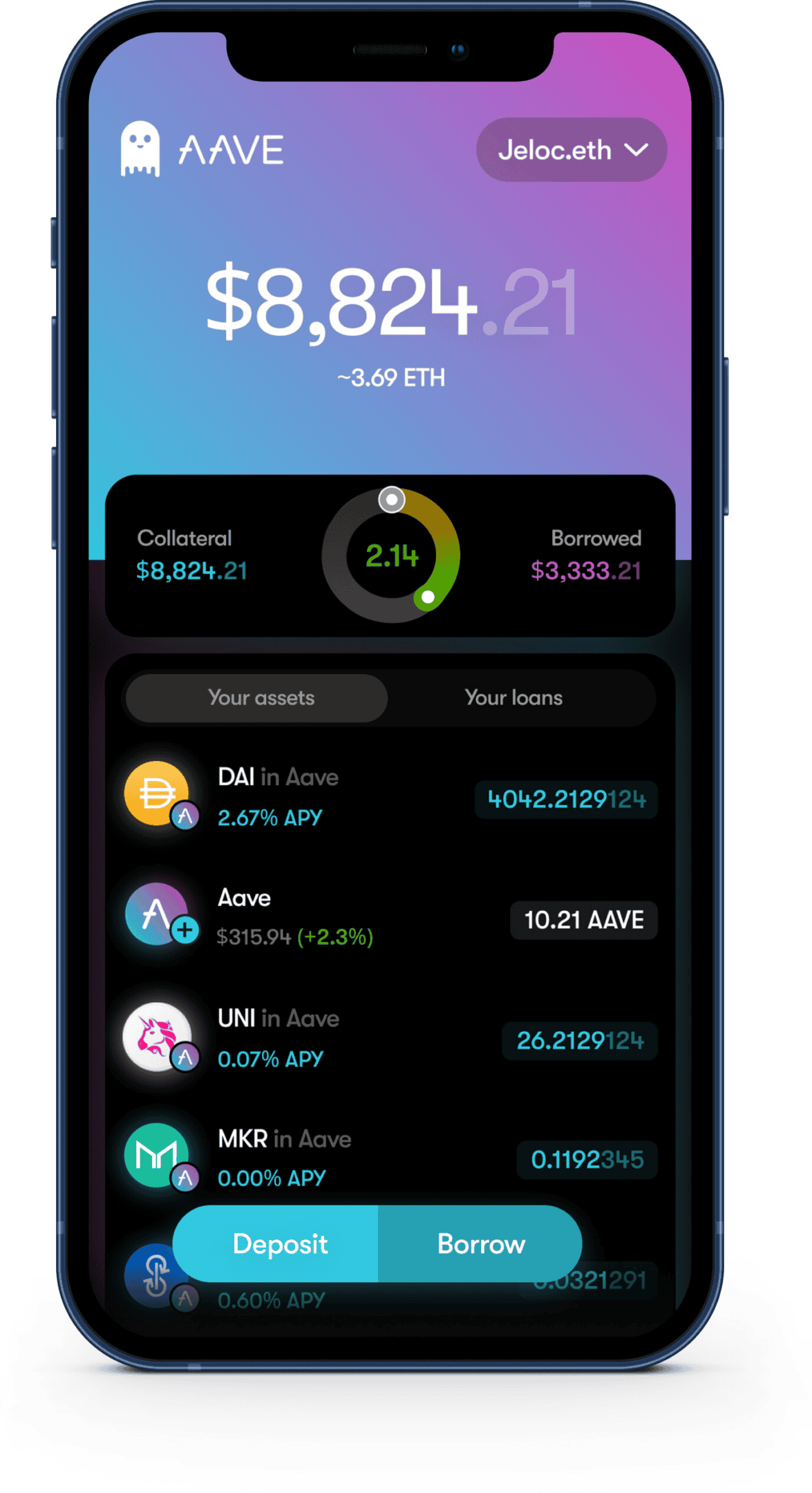
| 2 | Aave | Lending & Borrowing | Ethereum, Polygon, Avalanche | Borrow and lend a variety of crypto assets with competitive interest rates. |
| 3 | Uniswap | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) | Ethereum | Swap tokens directly from your wallet with no intermediaries. |
| 4 | Curve Finance | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) | Ethereum | Trade stablecoins and other pegged assets with low slippage and fees. |
| 5 | MakerDAO | Stablecoin & Lending | Ethereum | Create and manage DAI, a decentralized stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. |
| 6 | Convex Finance | Yield Aggregator | Ethereum | Boost your CRV rewards and earn additional yield through staking. |
| 7 | PancakeSwap | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) | Binance Smart Chain | Trade a wide range of BEP-20 tokens on the Binance Smart Chain. |
| 8 | Compound | Lending & Borrowing | Ethereum | Earn interest on your crypto assets or borrow against them. |
| 9 | SushiSwap | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) | Ethereum, Polygon, Fantom, etc. | A community-driven DEX with a focus on yield farming and liquidity provision. |
| 10 | Balancer | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) | Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum | Trade a diverse range of tokens with customizable liquidity pools. |
Note: The DeFi landscape is constantly evolving, and new projects and platforms emerge frequently. It’s essential to conduct your research and due diligence before interacting with any DeFi app.
Unraveling DeFi: A Beginner’s Guide
What is DeFi?
Decentralized finance, often shortened to DeFi, represents a revolutionary shift in how we interact with financial services. At its core, DeFi aims to recreate traditional financial systems like banking, lending, and trading, but without the need for intermediaries like banks or brokers. It leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions in a transparent and secure manner.
Key Components of DeFi
- Blockchain Technology: The backbone of DeFi, ensuring immutability and transparency of transactions.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code.
- Decentralized Applications (DApps): Applications built on the blockchain that provide various financial services.
- Cryptocurrency: Digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security.
How Does DeFi Work?
DeFi operates on a decentralized network, eliminating the need for a central authority. Smart contracts automate and enforce the terms of financial agreements, ensuring trust and transparency. Users interact with DeFi platforms through DApps, accessing a wide array of services.
Benefits of DeFi
- Accessibility: Open to anyone with an internet connection, promoting financial inclusion.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, fostering trust and accountability.
- Security: Smart contracts reduce the risk of fraud and manipulation.
- Efficiency: Automated processes and reduced reliance on intermediaries lead to faster and cheaper transactions.
- Control: Users have full control over their assets and data.
Common DeFi Use Cases
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading platforms.
- Lending and Borrowing Platforms: Enable users to lend their crypto assets and earn interest or borrow funds against their holdings.
- Yield Farming: A strategy to maximize returns by providing liquidity to DeFi protocols.
- Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to the value of a stable asset, like the US dollar, to minimize volatility.
Risks and Challenges
While DeFi holds immense promise, it’s important to be aware of the associated risks:
- Smart Contract Risks: Bugs or vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to exploits and financial losses.
- Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is known for its price fluctuations, which can impact the value of DeFi assets.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape for DeFi is still evolving, creating potential legal and compliance challenges.
Getting Started with DeFi
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the basics of blockchain, cryptocurrency, and smart contracts.
- Choose a Wallet: Select a secure wallet to store your crypto assets.
- Explore DeFi Platforms: Research and choose reputable DeFi platforms that align with your needs.
- Start Small: Begin with a small investment and gradually increase your exposure as you gain confidence and experience.
The Future of DeFi
DeFi has the potential to disrupt traditional finance and reshape the global financial landscape. As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks become clearer, DeFi is expected to see wider adoption and integration into mainstream financial systems.
Understanding the Basics of DeFi
DeFi revolutionizes finance by removing middlemen and using blockchain technology. It lets people access financial services directly through smart contracts. This new system aims to be more open and fair than traditional banking.
Decentralized vs. Centralized Finance
Decentralized finance differs greatly from centralized finance. Traditional banks control your money and data. DeFi puts control in users’ hands.
Key differences:
- No central authority in DeFi
- 24/7 access to services
- Lower fees due to no middlemen
- Anyone can join without approval
Centralized finance has some benefits:
- Customer support
- Regulation and insurance
- Easier to use for most people
DeFi offers more freedom but requires users to manage their own security.
The Blockchain Technology Foundation
Blockchain technology forms the base of DeFi. It’s a digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. This makes it very hard to change or hack.
Features of blockchain in DeFi:
- Transparency: All transactions are public
- Security: Cryptography protects data
- Immutability: Records can’t be altered
Popular blockchains for DeFi:
- Ethereum
- Binance Smart Chain
- Solana
Each blockchain has its own strengths and weaknesses for DeFi apps.
The Role of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing programs on the blockchain. They automatically carry out actions when certain conditions are met. In DeFi, smart contracts replace many functions of banks.
Examples of smart contract use in DeFi:
- Lending and borrowing
- Trading assets
- Insurance policies
Benefits of smart contracts:
- Speed: Transactions happen instantly
- Trust: No need for intermediaries
- Accuracy: Removes human error
Smart contracts power most DeFi applications. They enable complex financial services without human involvement.
Key Components of DeFi
DeFi systems rely on several core elements that work together to create a new financial ecosystem. These components enable users to engage in various financial activities without traditional intermediaries.
Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
Cryptocurrencies form the backbone of DeFi. Bitcoin and Ethereum are two of the most well-known digital assets. Ethereum plays a crucial role in DeFi due to its smart contract capabilities.
Users can buy, sell, and trade these digital tokens directly. This removes the need for banks or brokers. Cryptocurrencies offer faster transactions and lower fees compared to traditional money transfers.
Many DeFi platforms use their own tokens. These tokens often give holders voting rights on platform decisions. They may also provide other benefits like reduced fees or rewards.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
DEXs allow users to trade cryptocurrencies without a central authority. They use smart contracts to match buyers and sellers automatically. This removes the need for a middleman.
Popular DEXs include Uniswap and SushiSwap. These platforms often have lower fees than centralized exchanges. They also offer more privacy since users don’t need to create accounts or verify their identity.
DEXs use liquidity pools to facilitate trades. Users can add their tokens to these pools and earn fees from trades. This system is called automated market making (AMM).
Lending Protocols
DeFi lending protocols let users borrow and lend crypto assets directly. Compound and Aave are two well-known lending platforms. These systems use smart contracts to manage loans automatically.
Borrowers must provide collateral to get a loan. The collateral is often worth more than the borrowed amount. This helps protect lenders if borrowers can’t repay.
Lenders earn interest by adding their assets to lending pools. Interest rates adjust based on supply and demand. This creates a dynamic market for borrowing and lending.
Stablecoins and Synthetic Assets
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a steady value. They’re often pegged to a fiat currency like the US dollar. DAI is a popular decentralized stablecoin created by MakerDAO.
Stablecoins help reduce price volatility in DeFi transactions. They’re useful for trading, lending, and as a store of value. Many DeFi platforms use stablecoins as a base currency.
Synthetic assets are tokens that represent other assets. They can track the price of stocks, commodities, or currencies. These tokens let users gain exposure to traditional markets without leaving the DeFi ecosystem.
Exploring DeFi Applications
DeFi apps offer new ways to manage money and earn returns. They let users lend, borrow, trade, and invest without banks or middlemen.
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Yield farming involves lending crypto assets to earn rewards. Users put their tokens into liquidity pools on platforms like Uniswap or Compound. These pools power trading and lending services.
In return, users get a share of fees and extra tokens. This can lead to high returns, but it also comes with risks. The value of tokens can change fast. Smart contract bugs could cause losses.
Liquidity mining is similar. Platforms give out new tokens to people who add funds to their pools. This helps grow the platform and rewards early users.
Insurance and Risk Management
DeFi insurance protects users from hacks, bugs, and market crashes. Platforms like Nexus Mutual offer cover for smart contract failures. Users can buy policies to safeguard their funds.
Some projects also use prediction markets for risk management. These let people bet on future events, spreading out risk.
Insurance in DeFi is still new. It may not cover all types of losses. Users should read terms carefully before buying.
Asset Management Tools
DeFi asset management tools help users handle their crypto investments. They offer ways to track portfolios, rebalance holdings, and find new opportunities.
Some tools use automated market makers to trade assets. Others link to lending platforms to boost returns.
Many of these tools are non-custodial. This means users keep control of their funds. But it also puts more responsibility on the user to stay safe.
Asset management in DeFi can be complex. Users should start small and learn as they go.
Key Advantages and Challenges in DeFi
DeFi offers new financial opportunities but also comes with risks. It aims to make finance more open while tackling technical hurdles.
Decentralization and User Empowerment
DeFi gives users direct control of their money. There’s no need for banks or other middlemen. Anyone with internet access can use DeFi services. This opens up finance to people without bank accounts.
Users can lend, borrow, and trade 24/7. They don’t need permission from anyone. Smart contracts run everything automatically.
DeFi also lets users earn interest on their crypto. Rates are often higher than traditional banks. Some projects give out governance tokens. These let users vote on important decisions.
Transparency and Security Concerns
All DeFi transactions are public on the blockchain. This makes the system very open. Anyone can check what’s happening at any time.
But this openness can also be risky. Hackers might find weak spots in the code. If they do, they could steal lots of money.
Smart contracts need careful testing. Even small bugs can lead to big losses. Some projects use outside audits to check their security.
Scams are another problem in DeFi. New users should be careful. It’s easy to fall for fake projects that look real.
Interoperability and Scalability
Many DeFi projects work together. This creates a connected system of financial tools. Users can move assets between different services easily.
But as DeFi grows, some blockchains struggle to keep up. Transactions can get slow and expensive when there’s high demand.
Teams are working on solutions. Layer 2 networks and new blockchains aim to make DeFi faster and cheaper.
Cross-chain bridges let users move assets between different blockchains. This helps solve scaling issues. But these bridges can also be targets for attacks.
Getting Started with DeFi
DeFi offers new ways to manage money without banks. Users need a digital wallet to start. They must learn about fees and how to join online communities.
Setting Up a Wallet and Interacting with DApps
To use DeFi, you need a digital wallet. MetaMask is a popular choice. It’s easy to set up and use.
Steps to get started:
- Install MetaMask as a browser extension
- Create a new wallet
- Write down your seed phrase and keep it safe
- Add some cryptocurrency to your wallet
Once set up, you can connect to DeFi apps. These are called DApps. To use a DApp:
- Go to the DApp’s website
- Click “Connect Wallet”
- Choose MetaMask
- Approve the connection
Always be careful. Only connect to trusted DApps. Check the website address carefully.
Understanding Gas Fees and Transactions
Gas fees are charges for using the network. They pay for the work done by computers that run the network.
Key points about gas fees:
- Fees change based on how busy the network is
- You can choose higher fees for faster transactions
- Some networks have lower fees than others
When you make a transaction:
- Type in the amount you want to send
- Set your gas fee
- Confirm the transaction in your wallet
- Wait for the network to process it
Always double-check details before confirming. Transactions can’t be undone.
Learning About DeFi Community and Governance
Many DeFi projects let users take part in decision-making. This is called governance.
How to get involved:
- Buy governance tokens of a project you like
- Join the project’s forum or chat group
- Read proposals and share your thoughts
- Vote on changes using your tokens
Benefits of taking part:
- Help shape the future of the project
- Learn more about how DeFi works
- Meet others interested in DeFi
Start small. Learn as you go. Don’t invest more than you can afford to lose.
Frequently Asked Questions
DeFi offers new financial opportunities but can be complex for beginners. Here are answers to common questions about getting started with decentralized finance. These cover the basics, first steps, platforms, strategies, risks, and useful tools.
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and how does it work?
DeFi is a system of financial services that run on public blockchains. It works without banks or other middlemen. Users can lend, borrow, trade, and invest directly with each other.
DeFi uses smart contracts to automate transactions. These are computer programs that run when certain conditions are met. This allows for trustless operations without needing a central authority.
What are the first steps for a beginner to get started with DeFi?
Beginners should start by learning about cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Understanding these basics helps grasp DeFi concepts better.
Next, set up a cryptocurrency wallet. This is needed to interact with DeFi platforms. Popular options include MetaMask for desktop and Trust Wallet for mobile.
Lastly, buy some cryptocurrency. Ethereum is widely used in DeFi. Platforms like Coinbase or Binance allow purchases with regular money.
Which DeFi platforms are recommended for beginners to learn and invest?
Compound and Aave are good platforms for beginners. They offer simple ways to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies.
Uniswap is a user-friendly decentralized exchange. It allows trading different tokens without a middleman.
Yearn Finance provides easy access to yield farming. This is a way to earn rewards by lending cryptocurrencies.
What are some common investment strategies in Decentralized Finance?
Yield farming involves lending cryptocurrencies to earn interest. Users can move funds between platforms to get the best rates.
Liquidity providing means adding funds to trading pools on decentralized exchanges. Providers earn a share of trading fees.
Staking involves locking up cryptocurrencies to support network operations. This can earn rewards similar to interest.
How can one assess the risks and rewards when investing in DeFi?
Research the platform’s history, team, and security measures. Look for audited smart contracts and a strong track record.
Check the Annual Percentage Yield (APY) for potential returns. But remember, higher yields often come with higher risks.
Consider the volatility of cryptocurrencies. Rapid price changes can affect the value of DeFi investments.
Be aware of impermanent loss in liquidity pools. This can happen when asset prices change after providing liquidity.
What are some essential tools and resources for beginners in DeFi?
DeFi Pulse tracks the total value locked in various DeFi protocols. It helps compare different platforms.
CoinGecko and CoinMarketCap provide price data and market information for cryptocurrencies.
Etherscan allows users to check transactions and smart contract interactions on the Ethereum blockchain.
DeFi educational platforms like Finematics offer beginner-friendly guides and explanations of complex topics.